Visibility and Monitoring: Key Steps in the Zero Trust Journey

The Zero Trust Policy framework operates on the ideology that a complex network is always vulnerable and at-risk to internal and external threats. And, the policy enables the enterprise setups (you) to strategize and organize a thorough security approach to counter those threats.
However, by threats, we also imply the code or network vulnerabilities in your security system that can potentially escalate to threats or risks.
The essence of Zero Trust policy stems from two key aspects:
- Visibility: An entirely transparent vision (Zero Trust Visibility) into the various activities and events happening in the enterprise network and over or via the network entities.
- Monitoring: 24*7*365 monitoring of all the network entities (Activity Monitoring), identify the abnormal ones and strictly nip them in the bud, without a second’s delay.
So, if we assume the Zero Trust Security Model as a wheel, visibility and monitoring are the two key cogs that are indispensable for its functioning.
Here, we explore more on this in the following sections and discover how visibility and monitoring make the Zero Trust security approach infallible!
Let us begin with an understanding of how Zero Trust works.
How Does Zero Trust Work?
The Zero Trust Architecture was developed by John Kindervag (principal analyst at Forrester Research) in 2010. It is a broad framework focusing on 360-degree protection of an enterprise network, data, information and other valuable assets.
The framework protects the system against external and internal threats via:
- Close inspection and creating logs of the entire network traffic
- Limited and controlled access to enterprise network
- Proactive verification and network resources security
All the resources and data are inaccessible by default and are made accessible only for a limited time and under the right circumstances.
Every single connection is verified and authenticated before accessing or connecting with an application.
Hence, every interaction meets the conditional requirements of your security policies and every device gets authenticated and authorized. The same rule is applicable to the entire network flow and connection management.
Take a look at the following visual to understand this better:
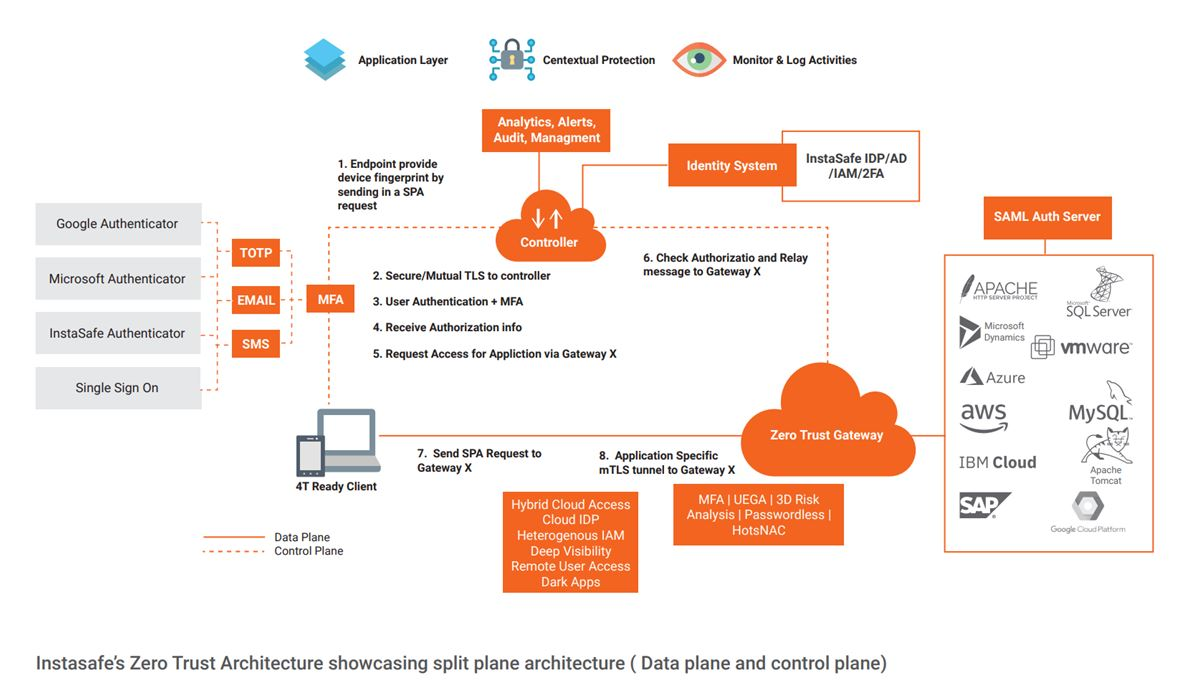
How to Successfully Implement Zero Trust in an Enterprise?
For successful implementation, an enterprise needs to connect each security domain in terms of information and data. All the security stakeholders must compile a set of priorities to agree upon and come up with access policies. All the connections to and from the enterprise network, devices, apps, workloads and data centres must be secured.
Hence, creating a well-planned strategy and carefully crafted roadmap is a must.
Further, the overall security measures must not impede the functioning and user or employee experience.
Now that we know what a Zero Trust Framework is and what is required for its successful implementation one question arises:
How do we ensure that the enterprise network remains in the state of ideal security and how to stop any threat?
The answer is – User Activity Monitoring and Zero Trust Visibility.
User Activity Monitoring: Zero Trust Journey’s Key Step #1
User Activity Monitoring or Activity Monitoring employs different tools to track and monitor User and Event/Entity Behavior over the enterprise network. Also termed as User and Event Behavior Analytics or UEBA, it allows the enterprises to understand how their network entities interact with their resources and data.
Hence, it keeps a check on the internal threats.
Activity monitoring stems from the “Never trust, always verify,” approach. This facilitates the successful implementation of the Zero Trust framework in an enterprise, as mentioned in the section above.
However, you must understand that this monitoring doesn’t end with identity confirmation, and also includes:
- Involving key stakeholders, such as worker advocates, legal and HR departments to ensure that no access or security loophole exists.
- Implementing controls and aids for monitoring.
- Set clear monitoring goals, such as identifying, tackling and resolving the security risk
- Set enterprise transparency regarding access rights and policies
- Offer limited access to monitored data
- Monitor one and all, even the monitors
Zero Trust Visibility: Zero Trust Journey’s Key Step #2
As Zero Trust reduces implicit trust and involves authentication and validation for every access and every user, visibility becomes a precondition for it. 100% visibility into all the information, data, network entities and traffic ensures successful implementation of the Zero Trust strategy.
Zero Trust Visibility implies that security professionals have a complete view of scenarios like – who is working on what, at what time, for what purpose and confirming the behaviour with allowed preset values.
Visibility analytics also enable you to eliminate blind spots and have a proper vision of all your network assets.
When your security and incident response teams have such extensive visibility, they can thoroughly monitor and track any behaviour or activity that can potentially harm your security. UEBA and visibility analytics are extremely crucial to ensure the safety and security of your enterprise network.
Stats report that more than 80% of enterprise attacks are a result of misuse or malicious use of user or entity credentials. Hence, it is important to have 100% visibility across all the user and entity credentials and attributes.
Some prominent user attributes and credentials that must be visible at all times are:
- Apps installed on endpoints
- Risk and Authentication protocol
- Type and functioning of endpoints
- Software and firmware versions and status
- Geo-location
- User and network entity behaviour patterns
- Number and type of privileges for each user on each device and for each asset
- Patch levels and status
- Incident detections
- User IDs (personal and programmed)
Laying the Groundwork for Zero Trust Enterprises: What Must Be on Your Agenda?
In your pursuit of establishing a Zero Trust security framework in your organization, it is important to plan your agenda with the right mindset. By now you might have realized that apart from the other aspects of a Zero Trust Security Model, you must have Visibility and Monitoring on your checklist.
Always remember, you cannot protect anything that is not completely visible or monitored. Hence, plan your Zero Trust strategy around monitoring and visibility.
Key Products
Zero Trust Application Access | Zero Trust Network Access | Multi Factor Authentication | IAM Identity And Access Management | Secure Enterprise Browser
Key Features
SSO Single Sign On | Endpoint Security | Contextual Based Access Controls | Always On VPN Connection |Clientless VPN | Device Binding | Device Posture Check | Domain Joining
Key Solutions
VPN Alternative Technology | Secure Remote Access Solutions | Cloud Application Security | DevOps Security | VoIP Security Solutions
