How Zero Trust Can Protect You from Lateral Movement Attacks?
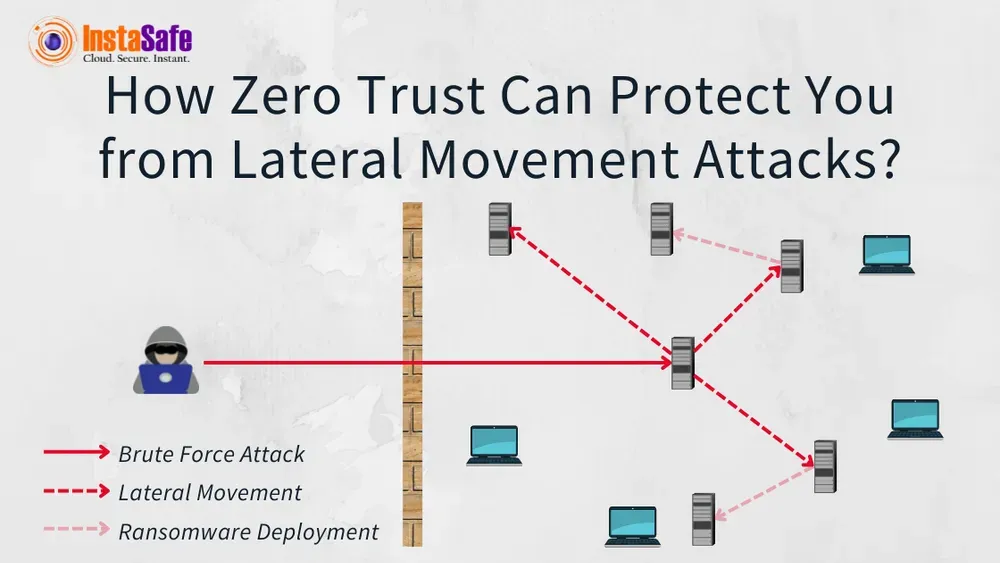
Organisations today face sophisticated threats that break in but do not immediately cause damage. Instead, cybercriminals play a longer, more strategic game. When they compromise one endpoint, they use that foothold to move deeper into your network— a technique known as lateral movement.
Understanding this threat and implementing modern security approaches like Zero Trust can make the difference between a minor security incident and a catastrophic breach.
What is the Lateral Movement?
Lateral movement refers to the techniques cybercriminals use to expand their control throughout a network after their initial breach. What makes lateral movement particularly dangerous is how it allows attackers to disguise their activities as legitimate network traffic, making detection extremely difficult using conventional security tools.
Think of it like a burglar who breaks into a house through a window but then uses the interior doors to access every room. That initial entry point is just the beginning—the real damage happens when they move freely inside.
Three Stages of Lateral Movement Attacks
Reconnaissance
During this phase, attackers explore your network environment. They observe naming conventions, study network hierarchy, identify open firewall ports and map out weaknesses. Just as a thief might cause a neighbourhood before breaking in, cybercriminals gather intelligence to plan their deeper infiltration.
Infiltration
Using stolen login credentials— often obtained through phishing or social engineering — attackers employ privilege escalation techniques to gain access to different parts of your system. These credentials act as keys that unlock doors across your network infrastructure.
Access
Once attackers locate their target systems or data, they execute their ultimate objective. This might involve delivering ransomware, stealing sensitive information or establishing persistent backdoors for future attacks.
How Zero Trust Disrupts Lateral Movement?
A Zero Trust architecture enforces strict access policies based on contextual factors—including user identity, device health, location and requested data—effectively blocking inappropriate access and lateral movement throughout your environment.
- MicroSegmentation
Microsegmentation is a network security practice that creates secure zones within data center environments by segmenting application workloads into intelligent groupings and securing them individually.
Microsegmentation can assist in preventing cybersecurity attacks in lateral movement since it aligns with the principles of Zero Trust Security, which enforces proper authorization and validation for limited access to applications, data, or systems.
2. Least Privilege Access
Users get access to resources on a “Need to Know basis”. Users with authorized devices get access to authorized applications. IT administrators can set granular access controls for users.
3. Multi Factor Authentication
Multi factor authentication provides an extra layer of authentication alongside username and password for security against lateral movement attacks. Second level authentication can be OTP over SMS / Email, TOTP or push notifications.
Zero Trust can contain the spread of lateral movement security attacks.Even if a user or his device is compromised and gets access to one part of the network, the hacker will not be able to spread across the entire network. Visit our official website today to learn more about InstaSafe’s Zero Trust Security solutions.
4. Continuous Verification
Zero Trust does not just check credentials once. It constantly monitors all connections, validating security status throughout the entire session to immediately detect and respond to suspicious changes in user behaviour or device status.
- Visibility and Control
Zero Trust demands complete transparency across all network traffic—even encrypted communications—allowing security teams to identify anomalies, enforce consistent policies and maintain comprehensive oversight of all resource access throughout the environment.
How to Prevent Lateral Movement?
Best Prevention Strategies
- Implement Strong Endpoint Security: With today's hybrid work environments, robust endpoint and mobility solutions that enable zero trust access control, threat detection, and response across diverse devices are essential.
- Protect High-Value Targets: Accounts with administrative privileges represent prime targets because they provide access to your most sensitive data. These accounts should receive the highest levels of security protection and be used only for tasks requiring elevated privileges.
- Deploy Microsegmentation: This technique creates secure zones that isolate workloads from one another. By establishing granular segments tailored to specific traffic needs, you can limit network and application flows between workloads to only those explicitly permitted.
- Adopt a Security-First Zero Trust Approach: Security responsibility should extend beyond IT teams to everyone in your organisation. When all staff understand and follow basic security protocols within a zero-trust framework, your overall risk of cyberattacks decreases significantly.
Detection Strategies
- Monitor Login Activity: Closely tracking authentication traffic can help detect direct compromises and credential theft before attackers can cause significant damage.
- Run Behavior Analytics: Machine learning systems can establish baselines of normal user behaviour and flag suspicious deviations that might indicate a cyberattack in progress.
- Use Deception Technology: Deploying realistic decoy assets in your network creates traps for cybercriminals. When attackers interact with these decoys, they trigger silent alarms without realising they have been detected.
- Employ Threat Hunting: Proactively detecting unknown dangers in your network, usually via managed services, offers strong protection against sophisticated, covert assaults.
Implementing Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) represents a modern approach to securing applications and resources. Instead of relying on traditional VPNs that often grant excessive network access, ZTNA places a security boundary around each application and enforces Zero Trust policies on a per-user, per-application basis.
This granular approach creates effective segmentation between applications. If an attacker somehow bypasses authentication and access policies for one application, their reach remains limited to that specific application, preventing further lateral movement into your network.
Conclusion
Lateral movement remains one of the most dangerous techniques in a cybercriminal's arsenal. By understanding how these attacks unfold and implementing modern security approaches centred around zero-trust principles, organisations can dramatically reduce their risk exposure.
Protect your network from sneaky hackers with InstaSafe multi-factor authentication. Beyond just passwords, it adds extra security layers like SMS codes or push notifications. Stop lateral movement attacks with Multi-factor authentication before they spread, keeping your sensitive data safe.
Key Products
MFA | I&AM | ZTNA | Zero Trust Application Access | Secure Enterprise Browser
Key Features
Single Sign On | Endpoint Security | Device Binding | Domain Joining | Always On VPN | Contextual Based Access | Clientless Remote Access | Device Posture Check
Key Solutions
VPN Alternatives | DevOps Security | Cloud Application Security | Secure Remote Access | VoIP Security
