Zero Trust: Least Privilege Access Models
The concept of least privilege has been around the world well before its advent into cybersecurity. The famous ‘This is on a need to know basis, and you don't need to know’ phrase used in government and corporate settings has found itself occupying a position of importance in the world of network security today.
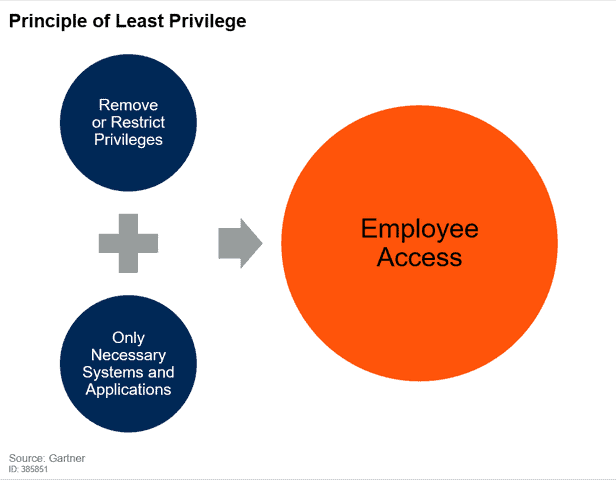
Simply put, the least privilege access model restricts access rights for all users, systems, and computing processes, allowing access only to those resources that are required by them to perform their routine activities. A traditional security model tends to accord some level of privilege to certain users, allowing them to bypass some security constraints. Least Privilege Models, however, accord the minimum clearance level to every user, that allow them to perform their roles. And the model is not only limited to users, but also applicable to devices, processes, and applications.
In a Zero Trust Architecture, the ‘need to know’ model plays an important role in negating the inherent trust we assign to certain devices. With leading market agencies estimating that almost 4/5ths of the total security breaches find their roots in privileged credentials, Zero Trust advocates a total discard of the concept of default trust and also relies on granular level access control functions to accord access on a need to know basis.
Privilege assignment may be done taking into account a multitude of factors, including the vertical in which the employee works, or her job function. Zero Trust Models, however, can’t be interchanged with the least privilege access model, because Zero Trust advocates the granting of least privilege only when certain conditions are met and answered positively. This is known as verification of contextual variables, and each request is considered with verification of queries including:
- Who are we granting access to
- What encompasses the context of the request
- What is the assessed risk of the access environment
Thus, in Zero Trust, privileges are entirely removed. The following considerations are taken into account:
- Distinctions between “inside” and “outside” the network perimeters no longer stand true. Network locality can’t be an alone factor in determining trust.
- Malicious threats exist on the network at all times and may be internal or external.
- Every user, device, network, and data, is to be validated and authenticated before granting access
In effect, adoption of, and the modification of the least privilege principle to remove all privileges and allow employees to access only what they are allowed to access help in significantly minimizing the attack surface since attackers are unable to access large amounts of data using just one compromised account. This, along with microsegmentation done by Zero Trust systems, helps in minimizing attack probability and securing your security setup
We are transforming the world of secure network access and helping businesses of all industries and sizes securely move to the cloud and empower their modern, mobile workforce. Our knowledgeable and experienced team comes together every day to deliver a truly innovative SaaS service and create a one-stop-shop for cybersecurity offerings. We are transforming the world of secure network access and helping businesses of all industries and sizes securely move to the cloud and empower their modern, mobile workforce. Our knowledgeable and experienced team comes together every day to deliver a truly innovative SaaS service and create a one-stop-shop for cybersecurity offerings.
We are transforming the world of secure network access and helping businesses of all industries and sizes securely move to the cloud and empower their modern, mobile workforce. Our knowledgeable and experienced team comes together every day to deliver a truly innovative SaaS service and create a one-stop-shop for cybersecurity offerings.
Key Products
MFA | I&AM | ZTNA | Zero Trust Application Access | Secure Enterprise Browser
Key Features
Single Sign On | Endpoint Security | Device Binding | Domain Joining | Always On VPN | Contextual Based Access | Clientless Remote Access | Device Posture Check
Key Solutions
VPN Alternatives | DevOps Security | Cloud Application Security | Secure Remote Access | VoIP Security
