How Zero Trust Access overcome latency and performance issues with VPN?

A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is used by most organizations for their remote employees who need to access corporate applications or servers from anywhere. VPNs are a popular and preferred method to access private networks using public networks. The popularity of VPNs is due to the fact that the technology is relatively simple to set up and easy to use. But VPN technology comes with its own set of challenges with respect to reliability and security aspects.
With more and more employees working from home, disconnection issues with VPN were quite common, which created various challenges for IT administrators and resentment among employees.
Let's understand why the disconnection occurs with VPNs.
VPN client software and VPN server send each other encrypted data or signed ping data every 10 seconds to communicate with each other with their active status. If the client software doesn’t receive a ping packet for more than 120 seconds, the client assumes that the server is not available and the communication is disconnected. This can happen if the ping packet is lost or gets blocked. An unreliable internet connection can cause packet loss and packets can get blocked during packet filtering by the router.
Disconnection can also happen if there are issues either with the user device settings or server or network. There could be multiple reasons that trigger disconnection. With regard to user device settings, if the user device stays ideal and gets into sleep mode, then the connection can be lost. If there are a lot of users connecting to the server and the amount of data flow is huge, it can cause bandwidth issue with the server, which leads to VPN disconnection.
There is one more major issue with VPN, i.e., latency. Latency is the amount of time between when a user performs an action and when they receive the response. For example, if a user clicks on an image, the time it takes for the image to load is latency. The loading or response time can be more or less dependent on the location of the VPN server and the data server. Suppose there is a user in India, a VPN server in Australia, and a data server in Singapore. Then the encrypted data packet will go from India to Australia, the data will be decrypted, and then it will move to Singapore. It will follow the reverse path for getting the response. These long travel time can cause VPN latency issues, which can be avoided by connecting to the VPN server nearest to the user and even best way is to connect user directly to the data server using an encrypted tunnel.
VPNs are also insecure as they expose entire networks to threats. The excessive trust issue with VPN and lack of granular access controls can pose significant risks to the network once the user is compromised.
How User Performance Gets Affected With Other Remote Access Solutions?
Not just VPN, other traditional remote access solutions also affect the user performance of a business, such as:
- RDP - RDP or remote desktop protocol is acquired by businesses to provide office desktop experience to remote workers. It uses low latency connections by setting the network setups at the ends of protected networks and users. The configuration of RDP protocols is what contributes to latency. Most businesses utilise the RDP network to offer efficient support to the workforce by consolidating network traffic. However, when the number of users rises, it starts creating issues. Not just this, RDP also exposes the network to the public internet by broadcasting the presence, which eases the cybercriminal's jobs to exploit the network.
- SD-WAN -Software-defined wide area network or SD-WAN is a new technology to secure the network, but its hardware and location shortcomings affect the latency. Furthermore, the transport and internet routing protocols are not optimised for the user performance because the data packet moves from network to network.
Other than this, these traditional network solutions interfere with the job of employees which involves utilising the communication platforms like teams, zooms, etc. These communication applications are an integral part of day-to-day office operations. However, these applications are susceptible to latency and can affect their performance. To overcome this, users generally turn off the VPN connection, and this exposes the network to security breaches.
Avoiding latency issues with InstaSafe Zero Trust Access:
Instasafe Zero Trust architecture is a split plane architecture where there is a separate data plane and control plane. After the user and device authentication gets completed, the user device is directly connected to the application through zero-trust gateway through an encrypted tunnel without having to route through any other intermediary server. This eliminates the latency issue arising from the backhauling of traffic.
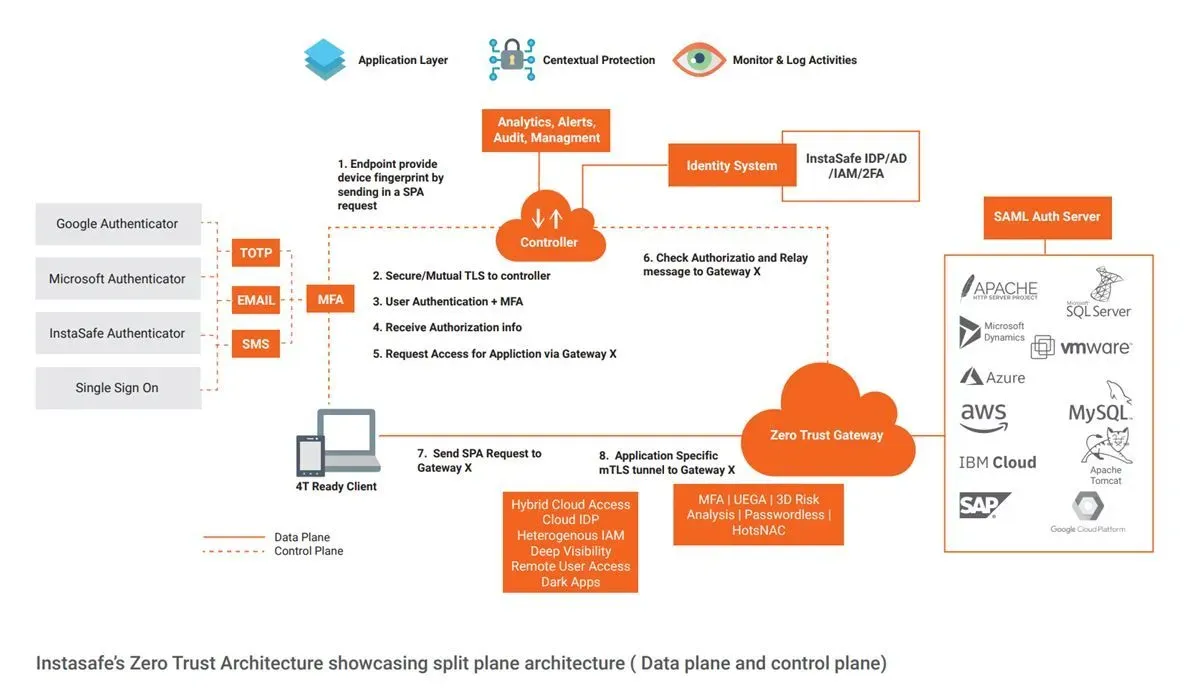
Zero Trust is an entirely cloud delivered solution. Multiple gateways can be configured which can handle a large number of concurrent users and intelligent routing. Zero Trust Access also addresses the security challenges of VPNs with granular access control mechanism that ensure right users can access authorized applications and not the entire network.
How Zero Trust Network Access Helps in Enhancing Performance?
The new security framework zero trust network access overcomes all the traditional security solution shortcomings. It offers a more secure and simpler network security structure to businesses. Below are some of the reasons how ZTNA improves the performance without compromising the security:
- Split Tunnelling - ZTNA makes use of split tunnelling to enhance the performance. It means the user can bypass the sensitive data through the encrypted path and general traffic over the public internet.
- Point-to-Point Topology -The ZTNA architect utilises point-to-point topology to establish a connection between accessing the resource and the user rather than passing it through a gateway. It helps in avoiding the backhaul and congestion that is generally linked to VPN security solutions. It means when a user accesses a resource on the cloud, the ZTNA creates a direct encrypted path for accessing the resources.
For more information, book a demo using this link: https://instasafe.com/book-a-demo
Key Products
Multi Factor Authentication | Identity And Access Management | ZTNA | Zero Trust Application Access | Secure Enterprise Browser
Key Features
Single Sign On | Endpoint Security | Device Binding | Domain Joining | Always On VPN | Contextual Access | Clientless Remote Access | Device Posture Check
Key Solutions
VPN Alternatives | DevOps Security | Cloud Application Security | Secure Remote Access | VoIP Security
